Page 67 - 5010
P. 67
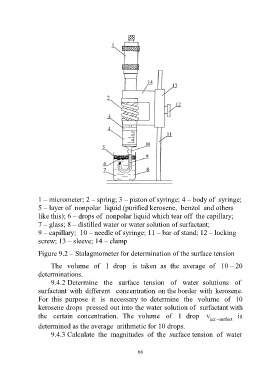
1 – micrometer; 2 – spring; 3 – piston of syringe; 4 – body of syringe;
5 – layer of nonpolar liquid (purified kerosene, benzol and others
like this); 6 – drops of nonpolar liquid which tear off the capillary;
7 – glass; 8 – distilled water or water solution of surfactant;
9 – capillary; 10 – needle of syringe; 11 – bar of stand; 12 – locking
screw; 13 – sleeve; 14 – clamp
Figure 9.2 – Stalagmometer for determination of the surface tension
The volume of 1 drop is taken as the average of 10 – 20
determinations.
9.4.2 Determine the surface tension of water solutions of
surfactant with different concentration on the border with kerosene.
For this purpose it is necessary to determine the volume of 10
kerosene drops pressed out into the water solution of surfactant with
the certain concentration. The volume of 1 drop V is
ker surfact
determined as the average arithmetic for 10 drops.
9.4.3 Calculate the magnitudes of the surface tension of water
66