Page 67 - 4749
P. 67
1
;
1 1 2 3
E
1
; (3.25)
2 2 3 1
E
1
.
3 3 1 2
E
The dependences (3.25) express the generalized Hooke's law
for an isotropic body.
3.8 Changing the volume of the body in deformation
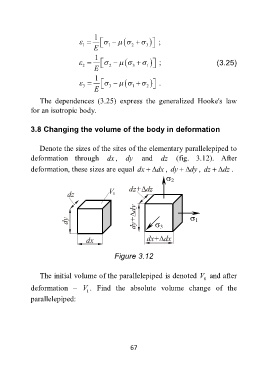
Denote the sizes of the sites of the elementary parallelepiped to
deformation through dx , dy and dz (fig. 3.12). After
deformation, these sizes are equal dx dx , dy dy , dz dz .
2
dz+ dz
dz V 0
dy
dy dy+ 3 1
dx dx+ dx
Figure 3.12
The initial volume of the parallelepiped is denoted V and after
0
deformation – V . Find the absolute volume change of the
1
parallelepiped:
67