Page 85 - 4624
P. 85
/
conditions. Furthermore, since Wa r is generally very small
compared to µ k W , the force needed to roll a cylinder over the surface
will be much less than that needed to slide it across the surface. It is
for this reason that a roller or ball bearings are often used to minimize
the frictional resistance between moving parts.
VII* TRUSSES
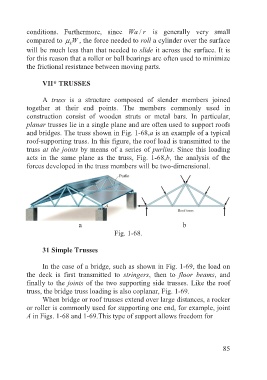
A truss is a structure composed of slender members joined
together at their end points. The members commonly used in
construction consist of wooden struts or metal bars. In particular,
planar trusses lie in a single plane and are often used to support roofs
and bridges. The truss shown in Fig. 1-68,a is an example of a typical
roof-supporting truss. In this figure, the roof load is transmitted to the
truss at the joints by means of a series of purlins. Since this loading
acts in the same plane as the truss, Fig. 1-68,b, the analysis of the
forces developed in the truss members will be two-dimensional.
a b
Fig. 1-68.
31 Simple Trusses
In the case of a bridge, such as shown in Fig. 1-69, the load on
the deck is first transmitted to stringers, then to floor beams, and
finally to the joints of the two supporting side trusses. Like the roof
truss, the bridge truss loading is also coplanar, Fig. 1-69.
When bridge or roof trusses extend over large distances, a rocker
or roller is commonly used for supporting one end, for example, joint
A in Figs. 1-68 and 1-69.This type of support allows freedom for
85