Page 44 - 4587
P. 44
c. Reclosers: devices similar in function to circuit breakers,
except they also have the ability to reclose after opening,
open again, and reclose again, repeating this cycle a
predetermined number of times until they lockout.
d. Fuses: devices that can carry a defined load current without
deterioration and interrupt a defined short-circuit current.
Circuit breakers, reclosers, and fuses are protection
devices. Often, switches are used on the high side of the
transformer, and protection devices are used on the low
side, but substations supplying large amounts of load may
have protection devices on both sides of the transformer.
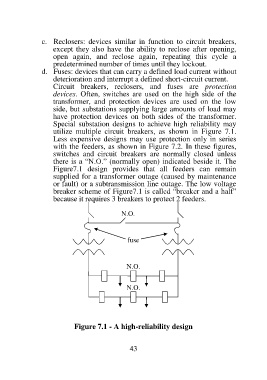
Special substation designs to achieve high reliability may
utilize multiple circuit breakers, as shown in Figure 7.1.
Less expensive designs may use protection only in series
with the feeders, as shown in Figure 7.2. In these figures,
switches and circuit breakers are normally closed unless
there is a “N.O.” (normally open) indicated beside it. The
Figure7.1 design provides that all feeders can remain
supplied for a transformer outage (caused by maintenance
or fault) or a subtransmission line outage. The low voltage
breaker scheme of Figure7.1 is called “breaker and a half”
because it requires 3 breakers to protect 2 feeders.
N.O.
fuse
N.O.
N.O.
Figure 7.1 - A high-reliability design
43