Page 48 - 4587
P. 48
voltage assigned to that class. For example, an insulator of voltage
class 15 kV may utilized in a 12.47kV, 13.2kV, and 13.8kV
system. There are four major distribution-level voltage classes:
5kV, 15kV, 25kV, and 35kV. The 15kV voltage class is the most
prevalent.
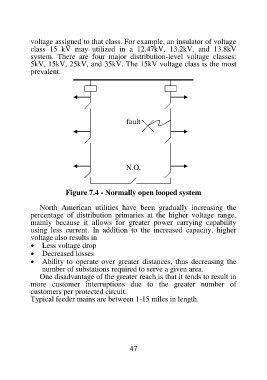
fault
N.O.
Figure 7.4 - Normally open looped system
North American utilities have been gradually increasing the
percentage of distribution primaries at the higher voltage range,
mainly because it allows for greater power carrying capability
using less current. In addition to the increased capacity, higher
voltage also results in
Less voltage drop
Decreased losses
Ability to operate over greater distances, thus decreasing the
number of substations required to serve a given area.
One disadvantage of the greater reach is that it tends to result in
more customer interruptions due to the greater number of
customers per protected circuit.
Typical feeder mains are between 1-15 miles in length.
47