Page 60 - 4498
P. 60
temperature. At high pressure real gases are less compressible than ideal
ones. The specific heat capacity and the viscosity of real gases differ from
properties of ideal gases. The main reason is connected with the behavior
of real gas molecules: they interact. Forces of interaction have electro-
magnetic and quantum nature.
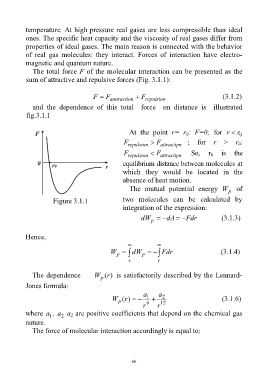
The total force F of the molecular interaction can be presented as the
sum of attractive and repulsive forces (Fig. 3.1.1):
F F annraction F repulsion (3.1.2)
and the dependence of this total force on distance is illustrated
fig.3.1.1
At the point r= r : F=0; for r
r
0
0
F repulsion F attractipn ; for r > r :
0
F repulsion F attractipn So, r is the
0
equilibrium distance between molecules at
which they would be located in the
absence of heat motion.
The mutual potential energy W of
p
Figure 3.1.1 two molecules can be calculated by
integration of the expression:
dW dA Fdr (3.1.3)
p
Hence,
W p dW p Fdr (3.1.4)
r r
The dependence W p (r ) is satisfactorily described by the Lennard-
Jones formula:
a a
W p (r ) 1 2 (3.1.6)
r 6 r 12
where a , a a are positive coefficients that depend on the chemical gas
2
2
1
nature.
The force of molecular interaction accordingly is equal to:
60