Page 27 - 6880
P. 27
treatment facilities. Also, this method can be applied for the computation of the
minimum height of the chimney at the industrial enterprise.
4 TASK OF CLASS
4.1 Before meeting on class, students should study basic theory of dispersion
of toxic substances into the atmosphere. All students are expected to come to class
alert and ready to participate in discussion.
4.2 Students in the classroom at the request of a teacher give answers on the
questions.
4.3 Then the students should solve the problems and tasks (should determine
the maximum near-surface concentrations of harmful substances, the distance from
the single emitted source, construct a graph of concentration of harmful substances
on the distance from the source of emission etc.) according to the variant given by
teacher. They may use references [1, 2] and theoretical data from basic theory.
Task 4.1
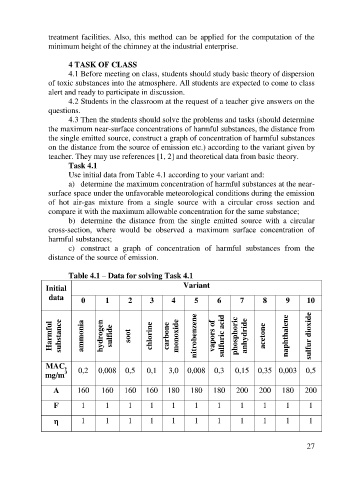
Use initial data from Table 4.1 according to your variant and:
a) determine the maximum concentration of harmful substances at the near-
surface space under the unfavorable meteorological conditions during the emission
of hot air-gas mixture from a single source with a circular cross section and
compare it with the maximum allowable concentration for the same substance;
b) determine the distance from the single emitted source with a circular
cross-section, where would be observed a maximum surface concentration of
harmful substances;
c) construct a graph of concentration of harmful substances from the
distance of the source of emission.
Table 4.1 – Data for solving Task 4.1
Initial Variant
data 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Harmful substance ammonia hydrogen sulfide soot chlorine carbone monoxide nitrobenzene vapors of sulfuric acid phosphoric anhydride acetone naphthalene sulfur dioxide
MAC,
3
mg/m 0,2 0,008 0,5 0,1 3,0 0,008 0,3 0,15 0,35 0,003 0,5
А 160 160 160 160 180 180 180 200 200 180 200
F 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
27