Page 89 - 6848
P. 89
Noise at work can cause other problems such as disturbance, interference with
communications, difficulties with concentration, fatigue, tension, and irritability – all
of which may also cause stress.
An emerging problem is voice loss due to the necessity to speak in noisy
environments and may affect, for example, teachers, lecturers and call center workers.
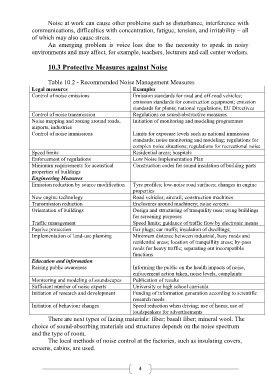
10.3 Protective Measures against Noise
Table 10.2 - Recommended Noise Management Measures
Legal measures Examples
Control of noise emissions Emission standards for road and off-road vehicles;
emission standards for construction equipment; emission
standards for plants; national regulations, EU Directives
Control of noise transmission Regulations on sound-obstructive measures
Noise mapping and zoning around roads, Initiation of monitoring and modeling programmes
airports, industries
Control of noise immissions Limits for exposure levels such as national immission
standards; noise monitoring and modeling; regulations for
complex noise situations; regulations for recreational noise
Speed limits Residential areas; hospitals
Enforcement of regulations Low Noise Implementation Plan
Minimum requirements for acoustical Construction codes for sound insulation of building parts
properties of buildings
Engineering Measures
Emission reduction by source modification Tyre profiles; low-noise road surfaces; changes in engine
properties
New engine technology Road vehicles; aircraft; construction machines
Transmission reduction Enclosures around machinery; noise screens
Orientation of buildings Design and structuring of tranquility uses; using buildings
for screening purposes
Traffic management Speed limits; guidance of traffic flow by electronic means
Passive protection Ear plugs; ear muffs; insulation of dwellings;
Implementation of land-use planning Minimum distance between industrial, busy roads and
residential areas; location of tranquillity areas; by-pass
roads for heavy traffic; separating out incompatible
functions
Education and information
Raising public awareness Informing the public on the health impacts of noise,
enforcement action taken, noise levels, complaints
Monitoring and modeling of soundscapes Publication of results
Sufficient number of noise experts University or high school curricula
Initiation of research and development Funding of information generation according to scientific
research needs
Initiation of behaviour changes Speed reduction when driving; use of horns; use of
loudspeakers for advertisements
There are next types of facing materials: fiber; basalt fiber; mineral wool. The
choice of sound-absorbing materials and structures depends on the noise spectrum
and the type of room.
The local methods of noise control at the factories, such as insulating covers,
screens, cabins, are used.
4