Page 104 - 6848
P. 104
radium) is simply a shorthand way of writing "37,000,000,000 disintegrations per
second", the rate of disintegration occurring in 1 gram of radium.
The more modern International System of Measurements (SI) unit for the same
type of measurement is the becquerel ( abbreviated "Bq" and named after Henri
Becquerel, the discoverer of radioactivity), which is simply a shorthand for "1
disintegration per second." To convert from curies to becquerels, multiply by 3.7 x
10
-11
10 . To convert from becquerels to curies, multiply by 2.7 x 10 .
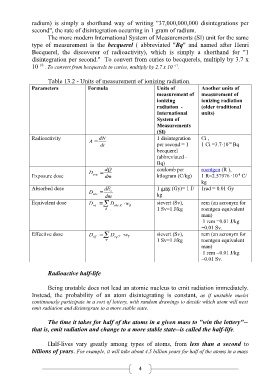
Table 13.2 - Units of measurement of ionizing radiation.
Parameters Formula Units of Another units of
measurement of measurement of
ionizing ionizing radiation
radiation - (older traditional
International units)
System of
Measurements
(SI)
Radioactivity dN 1 disintegration Cі ,
A 10
dt per second = 1 1 Cі =3.7·10 Bq
becquerel
(abbreviated -
Bq)
dQ coulomb per roentgen (R ),
D
-4
Еxposure dose exp dm kilogram (C/kg) 1 R=2.57976 ·10 C/
kg
Absorbed dose dE 1 gray (Gy)= 1 J/ 1rad = 0.01 Gy
D abs c
dm kg
Equivalent dose D eq D abs R w R sievert (Sv), rem (an acronym for
R 1 Sv=1 J/kg roentgen equivalent
man)
1 rem =0.01 J/kg
=0.01 Sv.
Effective dose D eff D eq T w T sievert (Sv), rem (an acronym for
T 1 Sv=1 J/kg roentgen equivalent
man)
1 rem =0.01 J/kg
=0.01 Sv.
Radioactive half-life
Being unstable does not lead an atomic nucleus to emit radiation immediately.
Instead, the probability of an atom disintegrating is constant, as if unstable nuclei
continuously participate in a sort of lottery, with random drawings to decide which atom will next
emit radiation and disintegrate to a more stable state.
The time it takes for half of the atoms in a given mass to "win the lottery"--
that is, emit radiation and change to a more stable state--is called the half-life.
Half-lives vary greatly among types of atoms, from less than a second to
billions of years. For example, it will take about 4.5 billion years for half of the atoms in a mass
4