Page 101 - 6848
P. 101
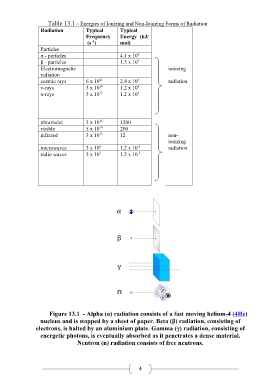
Table 13.1 - Energies of Ionizing and Non-Ionizing Forms of Radiation
Radiation Typical Typical
Frequency Energy (kJ/
-1
(s ) mol)
Particles
8
α - particles 4.1 x 10
7
β - particles 1.5 x 10
Electromagnetic ionizing
radiation
cosmic rays 6 x 10 21 2.4 x 10 9 radiation
8
γ-rays 3 x 10 20 1.2 x 10
x-rays 3 x 10 17 1.2 x 10
5
ultraviolet 3 x 10 1200
15
14
visible 5 x 10 200
infrared 3 x 10 13 12 non-
ionizing
-3
microwaves 3 x 10 9 1.2 x 10 radiation
radio waves 3 x 10 7 1.2 x 10
-5
Figure 13.1 - Alpha (α) radiation consists of a fast moving helium-4 (4He)
nucleus and is stopped by a sheet of paper. Beta (β) radiation, consisting of
electrons, is halted by an aluminium plate. Gamma (γ) radiation, consisting of
energetic photons, is eventually absorbed as it penetrates a dense material.
Neutron (n) radiation consists of free neutrons.
4