Page 74 - 6727
P. 74
Economic Theory
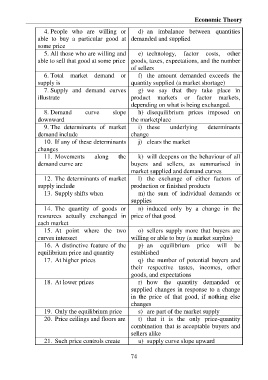
4. People who are willing or d) an imbalance between quantities
able to buy a particular good at demanded and supplied
some price
5. All those who are willing and e) technology, factor costs, other
able to sell that good at some price goods, taxes, expectations, and the number
of sellers
6. Total market demand or f) the amount demanded exceeds the
supply is quantity supplied (a market shortage)
7. Supply and demand curves g) we say that they take place in
illustrate product markets or factor markets,
depending on what is being exchanged.
8. Demand curve slope h) disequilibrium prices imposed on
downward the marketplace
9. The determinants of market i) these underlying determinants
demand include change
10. If any of these determinants j) clears the market
changes
11. Movements along the k) will deepens on the behaviour of all
demand curve are buyers and sellers, as summarised in
market supplied and demand curves
12. The determinants of market l) the exchange of either factors of
supply include production or finished products
13. Supply shifts when m) the sum of individual demands or
supplies
14. The quantity of goods or n) induced only by a change in the
resources actually exchanged in price of that good
each market
15. At point where the two o) sellers supply more that buyers are
curves intersect willing or able to buy (a market surplus)
16. A distinctive feature of the p) an equilibrium price will be
equilibrium price and quantity established
17. At higher prices q) the number of potential buyers and
their respective tastes, incomes, other
goods, and expectations
18. At lower prices r) how the quantity demanded or
supplied changes in response to a change
in the price of that good, if nothing else
changes
19. Only the equilibrium price s) are part of the market supply
20. Price ceilings and floors are t) that it is the only price-quantity
combination that is acceptable buyers and
sellers alike
21. Such price controls create u) supply curve slope upward
74