Page 74 - 6484
P. 74
finished product. Tailor-made clothing and custom-built houses include the customer
in all aspects of production, from product design to final acceptance, and involve
customer input in all key decisions. However, providing such individualized attention
to customers may not be feasible for firms with an industry-wide orientation. At the
other end of the customization scale, customers buying a new car, even in the budget
price category, can often choose not only the exterior and interior colors but also
accessories such as CD players, rooftop racks, and upgraded tires.
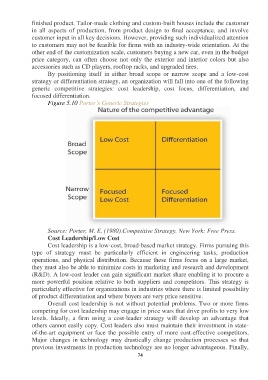
By positioning itself in either broad scope or narrow scope and a low-cost
strategy or differentiation strategy, an organization will fall into one of the following
generic competitive strategies: cost leadership, cost focus, differentiation, and
focused differentiation.
Figure 5.10 Porter’s Generic Strategies
Source: Porter, M. E. (1980).Competitive Strategy. New York: Free Press.
Cost Leadership/Low Cost
Cost leadership is a low-cost, broad-based market strategy. Firms pursuing this
type of strategy must be particularly efficient in engineering tasks, production
operations, and physical distribution. Because these firms focus on a large market,
they must also be able to minimize costs in marketing and research and development
(R&D). A low-cost leader can gain significant market share enabling it to procure a
more powerful position relative to both suppliers and competitors. This strategy is
particularly effective for organizations in industries where there is limited possibility
of product differentiation and where buyers are very price sensitive.
Overall cost leadership is not without potential problems. Two or more firms
competing for cost leadership may engage in price wars that drive profits to very low
levels. Ideally, a firm using a cost-leader strategy will develop an advantage that
others cannot easily copy. Cost leaders also must maintain their investment in state-
of-the-art equipment or face the possible entry of more cost-effective competitors.
Major changes in technology may drastically change production processes so that
previous investments in production technology are no longer advantageous. Finally,
74