Page 108 - 6484
P. 108
will succeed under each structure is also different. Research shows that when
employees work in product divisions in turbulent environments, because activities are
[9]
diverse and complex, their performance depends on their general mental abilities.
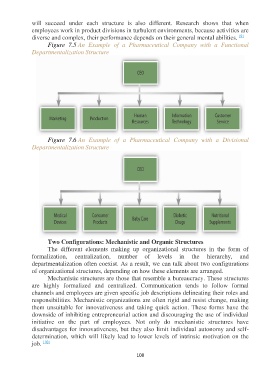
Figure 7.5 An Example of a Pharmaceutical Company with a Functional
Departmentalization Structure
Figure 7.6 An Example of a Pharmaceutical Company with a Divisional
Departmentalization Structure
Two Configurations: Mechanistic and Organic Structures
The different elements making up organizational structures in the form of
formalization, centralization, number of levels in the hierarchy, and
departmentalization often coexist. As a result, we can talk about two configurations
of organizational structures, depending on how these elements are arranged.
Mechanistic structures are those that resemble a bureaucracy. These structures
are highly formalized and centralized. Communication tends to follow formal
channels and employees are given specific job descriptions delineating their roles and
responsibilities. Mechanistic organizations are often rigid and resist change, making
them unsuitable for innovativeness and taking quick action. These forms have the
downside of inhibiting entrepreneurial action and discouraging the use of individual
initiative on the part of employees. Not only do mechanistic structures have
disadvantages for innovativeness, but they also limit individual autonomy and self-
determination, which will likely lead to lower levels of intrinsic motivation on the
job. [10]
108