Page 86 - 6437
P. 86
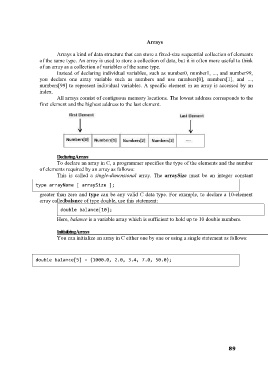
Arrays
Arrays a kind of data structure that can store a fixed-size sequential collection of elements
of the same type. An array is used to store a collection of data, but it is often more useful to think
of an array as a collection of variables of the same type.
Instead of declaring individual variables, such as number0, number1, ..., and number99,
you declare one array variable such as numbers and use numbers[0], numbers[1], and ...,
numbers[99] to represent individual variables. A specific element in an array is accessed by an
index.
All arrays consist of contiguous memory locations. The lowest address corresponds to the
first element and the highest address to the last element.
Declaring Arrays
To declare an array in C, a programmer specifies the type of the elements and the number
of elements required by an array as follows:
This is called a single-dimensional array. The arraySize must be an integer constant
type arrayName [ arraySize ];
greater than zero and type can be any valid C data type. For example, to declare a 10-element
array called balance of type double, use this statement:
double balance[10];
Here, balance is a variable array which is sufficient to hold up to 10 double numbers.
Initializing Arrays
You can initialize an array in C either one by one or using a single statement as follows:
double balance[5] = {1000.0, 2.0, 3.4, 7.0, 50.0};
89