Page 84 - 6437
P. 84
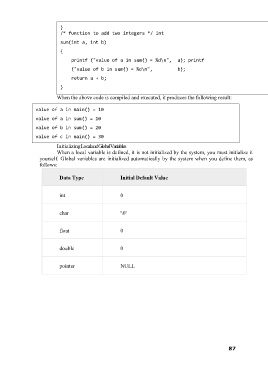
}
/* function to add two integers */ int
sum(int a, int b)
{
printf ("value of a in sum() = %d\n", a); printf
("value of b in sum() = %d\n", b);
return a + b;
}
When the above code is compiled and executed, it produces the following result:
value of a in main() = 10
value of a in sum() = 10
value of b in sum() = 20
value of c in main() = 30
Initializing Local and Global Variables
When a local variable is defined, it is not initialized by the system, you must initialize it
yourself. Global variables are initialized automatically by the system when you define them, as
follows:
Data Type Initial Default Value
int 0
char '\0'
float 0
double 0
pointer NULL
87