Page 13 - 6437
P. 13
Variables
A variable is nothing but a name given to a storage area that our programs can
manipulate. Each variable in C has a specific type, which determines the size and layout of the
variable's memory; the range of values that can be stored within that memory; and the set of
operations that can be applied to the variable.
The name of a variable can be composed of letters, digits, and the underscore character. It
must begin with either a letter or an underscore. Upper and lowercase letters are distinct because
C is case-sensitive. Based on the basic types explained in the previous chapter, there will be the
following basic variable types:
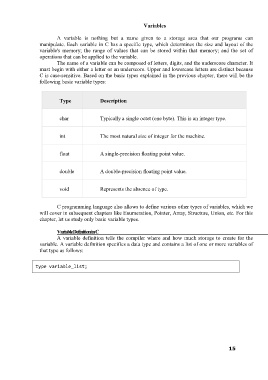
Type Description
char Typically a single octet (one byte). This is an integer type.
int The most natural size of integer for the machine.
float A single-precision floating point value.
double A double-precision floating point value.
void Represents the absence of type.
C programming language also allows to define various other types of variables, which we
will cover in subsequent chapters like Enumeration, Pointer, Array, Structure, Union, etc. For this
chapter, let us study only basic variable types.
Variable Definition in C
A variable definition tells the compiler where and how much storage to create for the
variable. A variable definition specifies a data type and contains a list of one or more variables of
that type as follows:
type variable_list;
15