Page 77 - 6273
P. 77
о
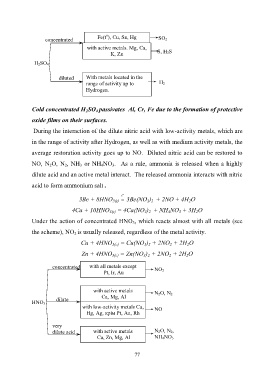
Fe(t ), Cu, Sn, Hg SO 2
concentrated
with active metals. Mg, Ca,
K, Zn S, H 2S
H 2SO 4
diluted With metals located in the
range of activity up to H 2
Hydrogen.
Cold concentrated H 2SO 4 passivates Al, Cr, Fe due to the formation of protective
oxide films on their surfaces.
During the interaction of the dilute nitric acid with low-activity metals, which are
in the range of activity after Hydrogen, as well as with medium activity metals, the
average restoration activity goes up to NO. Diluted nitric acid can be restored to
NO, N 2O, N 2, NH 3 or NH 4NO 3. As a rule, ammonia is released when a highly
dilute acid and an active metal interact. The released ammonia interacts with nitric
acid to form ammonium salt .
t o
3Be + 8HNO 3(s) 3Be(NO 3) 2 + 2NO + 4H 2O
4Ca + 10HNO 3(s) = 4Ca(NO 3) 2 + NH 4NO 3 + 3H 2O
Under the action of concentrated HNO 3, which reacts almost with all metals (see
the scheme), NO 2 is usually released, regardless of the metal activity.
Сu + 4HNО 3(c) = Cu(NО 3) 2 + 2NO 2 + 2H 2O
Zn + 4HNО 3(c) = Zn(NО 3) 2 + 2NO 2 + 2H 2O
concentrated with all metals except NO 2
Pt, Ir, Au
with active metals N 2O, N 2
Са, Mg, Al
dilute
HNO 3
with low-activity metals Cu, NO
Hg, Ag, крім Pt, Au, Rh
very
dilute acid with active metals N 2O, N 2,
Са, Zn, Mg, Al NH 4NO 3
77