Page 4 - 4911
P. 4
INTRODUCTION
Conserving energy is the best way to ensure a secure and sustainable energy supply
and to reduce greenhouse gases and emissions. Therefore the Ukraine has set itself the
objective of saving 20% energy until 2020 . Energy can be saved through increased
energy efficiency throughout the whole chain from its generation to its transmission and
distribution to more efficient end-use. One pillar for enhancing energy efficiency is
legislation: there is an increasingly stringent Ukrainian legislative framework on the
performance of products and buildings. Another pillar is research - paving the way for
breakthroughs allowing for more drastic energy savings in the medium and long term.
One of the most important ways of economy of fuel is the selection of rational types
of power plants and the rational arrangement them the best equipment, utilization of
secondary energy resources and ensure the necessary conditions for combustion of
heavy fuel oil, etc.
1. GAS TURBINE CYCLE
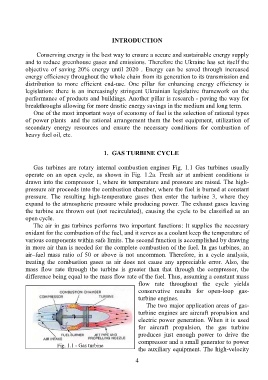
Gas turbines are rotary internal combustion engines Fig. 1.1 Gas turbines usually
operate on an open cycle, as shown in Fig. 1.2a. Fresh air at ambient conditions is
drawn into the compressor 1, where its temperature and pressure are raised. The high-
pressure air proceeds into the combustion chamber, where the fuel is burned at constant
pressure. The resulting high-temperature gases then enter the turbine 3, where they
expand to the atmospheric pressure while producing power. The exhaust gases leaving
the turbine are thrown out (not recirculated), causing the cycle to be classified as an
open cycle.
The air in gas turbines performs two important functions: It supplies the necessary
oxidant for the combustion of the fuel, and it serves as a coolant keep the temperature of
various components within safe limits. The second function is accomplished by drawing
in more air than is needed for the complete combustion of the fuel. In gas turbines, an
air–fuel mass ratio of 50 or above is not uncommon. Therefore, in a cycle analysis,
treating the combustion gases as air does not cause any appreciable error. Also, the
mass flow rate through the turbine is greater than that through the compressor, the
difference being equal to the mass flow rate of the fuel. Thus, assuming a constant mass
flow rate throughout the cycle yields
conservative results for open-loop gas-
turbine engines.
The two major application areas of gas-
turbine engines are aircraft propulsion and
electric power generation. When it is used
for aircraft propulsion, the gas turbine
produces just enough power to drive the
compressor and a small generator to power
Fig. 1.1 - Gas turbine
the auxiliary equipment. The high-velocity
4