Page 18 - 4798
P. 18
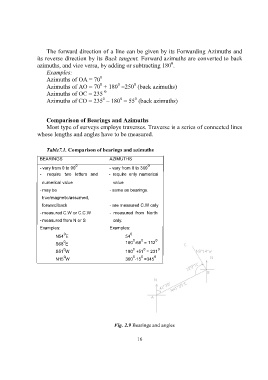
The forward direction of a line can be given by its Forwarding Azimuths and
its reverse direction by its Back tangent. Forward azimuths are converted to back
0
azimuths, and vice versa, by adding or subtracting 180 .
Examples:
0
Azimuths of OA = 70
0
0
0
Azimuths of AO = 70 + 180 =250 (back azimuths)
0
Azimuths of OC = 235
0
0
0
Azimuths of CO = 235 – 180 = 55 (back azimuths)
Comparison of Bearings and Azimuths
Most type of surveys employs traverses. Traverse is a series of connected lines
whose lengths and angles have to be measured.
Table7.1. Comparison of bearings and azimuths
BEARINGS AZIMUTHS
0
0
- vary from 0 to 90 - vary from 0 to 360
- require two letters and - require only numerical
numerical value value
- may be - same as bearings.
true/magnetic/assumed,
forward/back - are measured C.W only
- measured C.W or C.C.W - measured from North
- measured from N or S only.
Examples: Examples:
0 0
N54 E 54
0
0
0
0 180 -68 = 112
S68 E
0
0
0
0
S51 W 180 +51 = 231
0
0
0
0
N15 W 360 -15 =345
Fig. 2.9 Bearings and angles
16