Page 110 - 4749
P. 110
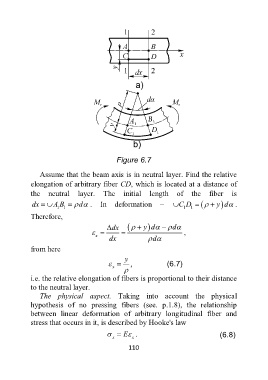
Figure 6.7
Assume that the beam axis is in neutral layer. Find the relative
elongation of arbitrary fiber CD, which is located at a distance of
the neutral layer. The initial length of the fiber is
dx A B d . In deformation – C D y d .
1 1 1 1
Therefore,
dx y d d
,
x
dx d
from here
y
, (6.7)
x
i.e. the relative elongation of fibers is proportional to their distance
to the neutral layer.
The physical aspect. Taking into account the physical
hypothesis of no pressing fibers (see. p.1.8), the relationship
between linear deformation of arbitrary longitudinal fiber and
stress that occurs in it, is described by Hooke's law
E . (6.8)
x x
110