Page 19 - 4624
P. 19
The tension force developed in a continuous cable which passes over
a frictionless pulley must have a constant magnitude to keep the cable
in equilibrium. Hence, for any angle θ shown in Fig. 1-8, the cable is
subjected to a constant tension T throughout its length.
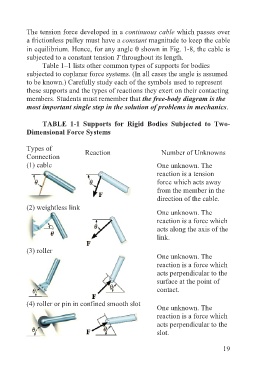
Table 1–1 lists other common types of supports for bodies
subjected to coplanar force systems. (In all cases the angle is assumed
to be known.) Carefully study each of the symbols used to represent
these supports and the types of reactions they exert on their contacting
members. Students must remember that the free-body diagram is the
most important single step in the solution of problems in mechanics.
TABLE 1-1 Supports for Rigid Bodies Subjected to Two-
Dimensional Force Systems
Types of Reaction Number of Unknowns
Connection
(1) cable One unknown. The
reaction is a tension
force which acts away
from the member in the
direction of the cable.
(2) weightless link
One unknown. The
reaction is a force which
acts along the axis of the
link.
(3) roller
One unknown. The
reaction is a force which
acts perpendicular to the
surface at the point of
contact.
(4) roller or pin in confined smooth slot
One unknown. The
reaction is a force which
acts perpendicular to the
slot.
19