Page 62 - 6880
P. 62
velocity of propagation of the shock wave in water than in air. At this time formed
a big wave.
The defeat of forest plantations and the destruction of the forest from the
blast wave depends on the power and type of ammunition, the distance from the
center (the epicenter) of an explosion, terrain, composition, fullness, thickness,
density and stand age. Lethality of a shock wave on the forest is characterized by
excessive pressure on her front. The degree of destruction of the forest may be
different from damage to branches and crowns to partial breaking of individual
trees and total destruction of the trees. The nature of the damage and destruction in
the woods can be different: the trees are broken at a height of 1-3 m from the
ground, pulled out by the roots and trunks can lie in the same direction, or in a
different overlay on each other.
In addition to the devastation, the shock wave is the cause of the fires that
occur as result of damage of power lines and gas systems, explosions of chemicals
and ammunition. In the case of the destruction of nuclear reactors possible
hazardous contamination of vast areas of radioactive substances.
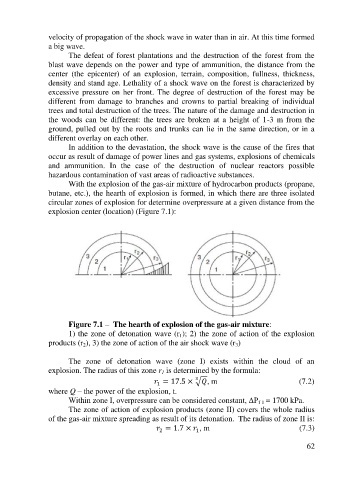
With the explosion of the gas-air mixture of hydrocarbon products (propane,
butane, etc.), the hearth of explosion is formed, in which there are three isolated
circular zones of explosion for determine overpressure at a given distance from the
explosion center (location) (Figure 7.1):
Figure 7.1 – The hearth of explosion of the gas-air mixture:
1) the zone of detonation wave (r ); 2) the zone of action of the explosion
1
products (r ), 3) the zone of action of the air shock wave (r )
3
2
The zone of detonation wave (zone I) exists within the cloud of an
explosion. The radius of this zone r is determined by the formula:
1
, m (7.2)
where Q – the power of the explosion, t.
Within zone I, overpressure can be considered constant, ΔP = 1700 kPa.
f I
The zone of action of explosion products (zone II) covers the whole radius
of the gas-air mixture spreading as result of its detonation. The radius of zone II is:
, m (7.3)
62