Page 43 - 6700
P. 43
Existence – for the question of why there is something and not nothing, see
being. The modern treatment of existence in the theory of *quantification is
sometimes put by saying that existence is not a predicate. The idea is that the
existential quantifier is itself an *operator on a predicate, indicating that the property
it expresses has instances. Existence is therefore treated as a second-order property,
or property of properties.
Matter – that which occupies space, possessing size and shape, mass,
movability, and solidity (which may be the same as impenetrability). Its nature was
historically one of the great subjects of philosophy, now largely pursued through the
philosophy of physics.
Space-time – the structure specified by treating space and time together as a
four-dimensional manifold. Points in space-time are called events. In the theory of
relativity, each event in space-time is associated with a past light cone (the set of past
events that could possibly have influenced it) and a future light cone (the set of future
events that it could possibly influence), where the possibility in question is limited by
the speed of light.
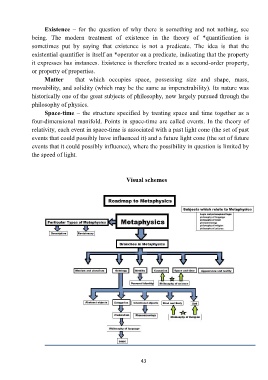
Visual schemes
43