Page 28 - 6437
P. 28
-
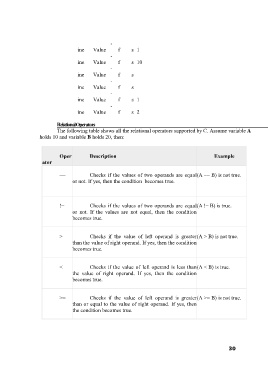
ine Value f s 1
-
ine Value f s 10
-
ine Value f s
-
ine Value f s
-
ine Value f s 1
-
ine Value f s 2
Relational Operators
The following table shows all the relational operators supported by C. Assume variable A
holds 10 and variable B holds 20, then:
Oper Description Example
ator
== Checks if the values of two operands are equal (A == B) is not true.
or not. If yes, then the condition becomes true.
!= Checks if the values of two operands are equal (A != B) is true.
or not. If the values are not equal, then the condition
becomes true.
> Checks if the value of left operand is greater (A > B) is not true.
than the value of right operand. If yes, then the condition
becomes true.
< Checks if the value of left operand is less than (A < B) is true.
the value of right operand. If yes, then the condition
becomes true.
>= Checks if the value of left operand is greater (A >= B) is not true.
than or equal to the value of right operand. If yes, then
the condition becomes true.
30