Page 22 - 6192
P. 22
5 DEMAND AND SUPPLY
1 The essence of demand as an economic category. Demand schedule and
curve. The law of demand. Determinants of demand.
2 The essence of supply as an economic category. Supply schedule and curve.
The law of supply. Determinants of supply.
3 The relationship between supply and demand and the establishment of the
market equilibrium price.
4 Elasticity of demand and supply, their types. Elasticity coefficients.
Key words: demand, supply, price, quantity demanded, quantity supplied, law
of demand, law of supply, equilibrium, excess supply, excess demand, elasticity
Economists use the term demand to refer to the amount of some good or
service consumers are willing and able to purchase at each price. Demand is based on
needs and wants – a consumer may be able to differentiate between a need and a
want, but from an economist’s perspective they are the same thing. Demand is also
based on ability to pay. If you cannot pay for it, you have no effective demand.
What a buyer pays for a unit of the specific good or service is called price. The
total number of units purchased at that price is called the quantity demanded. A rise
in price of a good or service almost always decreases the quantity demanded of that
good or service. Conversely, a fall in price will increase the quantity demanded.
Economists call this inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded the
law of demand.
Demand schedule is a tabular statement showing how much of a commodity is
demanded at different prices.
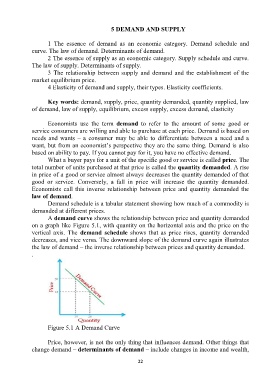
A demand curve shows the relationship between price and quantity demanded
on a graph like Figure 5.1, with quantity on the horizontal axis and the price on the
vertical axis. The demand schedule shows that as price rises, quantity demanded
decreases, and vice versa. The downward slope of the demand curve again illustrates
the law of demand – the inverse relationship between prices and quantity demanded.
.
Figure 5.1 A Demand Curve
Price, however, is not the only thing that influences demand. Other things that
change demand – determinants of demand – include changes in income and wealth,
22