Page 117 - 4714
P. 117
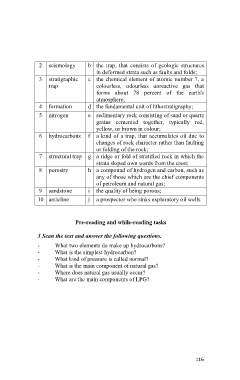
2 seismology b the trap, that consists of geologic structures
in deformed strata such as faults and folds;
3 stratigraphic c the chemical element of atomic number 7, a
trap colourless, odourless unreactive gas that
forms about 78 percent of the earth's
atmosphere;
4 formation d the fundamental unit of lithostratigraphy;
5 nitrogen e sedimentary rock consisting of sand or quartz
grains cemented together, typically red,
yellow, or brown in colour;
6 hydrocarbons f a kind of a trap, that accumulates oil due to
changes of rock character rather than faulting
or folding of the rock;
7 structural trap g a ridge or fold of stratified rock in which the
strata sloped own wards from the crest;
8 porosity h a compound of hydrogen and carbon, such as
any of those which are the chief components
of petroleum and natural gas;
9 sandstone i the quality of being porous;
10 anticline j a prospector who sinks exploratory oil wells.
Pre-reading and while-reading tasks
3 Scan the text and answer the following questions.
- What two elements do make up hydrocarbons?
- What is the simplest hydrocarbon?
- What kind of pressure is called normal?
- What is the main component of natural gas?
- Where does natural gas usually occur?
- What are the main components of LPG?
116